Effects of Smoking
Smoking affects the body as you smoke and over time. Learn the effects of smoking on your body and the potential illnesses associated such as lung cancer. Discover the different types of smoke, how different types of smoking affect the body, and treatment options for smoking.

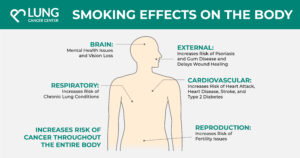
Effects of Smoking on the Lungs and Body
People expose themselves to a variety of toxins by smoking cigarettes, e-cigs, marijuana, and cigars, as well as inhaling external smoke. Others are exposed to secondhand smoke idly at work, out to eat, or at home, as they live with someone who smokes. Smoke can develop from burning plastic, wood, and chemicals that can lead to conditions such as lung cancer. No matter what you are smoking, there are harmful and dangerous side effects on the body. Lung cancer, strokes, or breathing issues are all potential side effects associated with smoke exposure. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says that smoking is the most common “preventable cause of death” in the U.S.
Smoking causes 9 out of 10 of all lung cancer deaths. On this page, we will explore the different types of smoke, the varieties of smoking devices, how smoking effects the lungs and body, as well as treatment options.
What Does Smoking Do to the Body?
Smoking affects every aspect of the body, from nearly every organ to the central nervous, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems, and hair, skin, and nails. Cigarettes were even made with asbestos at one time. Smoke has thousands of harmful chemicals and toxins that permanently alter body parts and can lead to serious conditions. Common side effects of smoking can include mental health issues, breathing issues, an increased heart rate, and much more.
How Does Smoking Affect the Lungs?
Although smoking affects the entire body, smoking has the greatest impact on the respiratory system. Smoking can cause lung disease by damaging your airways and the alveoli found in the lungs. Your body has over 500 million alveoli, and smoking kills the cells that line them. However, lung tissues do not grow back, unlike other parts of the body. Additionally, when you smoke, toxins damage lung tissues, which become fibrous. Fibrous lung tissues make it more difficult to fully expand your lungs and get enough air, leading to shortness of breath and chronic coughing.
Over time, smoking can lead to increased lung infections as well as a higher risk of conditions such as:
- Emphysema
- Chronic bronchitis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Lung cancer symptoms
Even those who do not smoke and inhale secondhand smoke from friends and family can have immediate negative effects on the body.
Immediate Effects of Smoking
When you inhale smoke, there are immediate, irreversible effects on the body. Whether you are smoking, around someone who smokes, or inhale smoke unintentionally, smoke can find a way to enter the body and make its way to the lungs. Even those representing our country on job sites or during incidents such as 9/11 can inhale asbestos and other dangerous chemical smoke. Once inside your body, smoke and its related toxins can permanently alter body functions such as your mental health, heart rate, and much more. Smoking health risks:
- Increased stress
- Altered brain chemistry
- Bronchospasms
- Increased phlegm productions
- Persistent dry cough
- Decreased physical performance
- Adverse lipid profile
- Atherosclerosis
- Thrombosis
- Constricted blood vessels
- Increased heart rate
- Increased blood pressure
- Gastroesophageal reflux
- Peptic ulcers
- Periodontal issues
- Halitosis
- Otitis media
- Sinusitis
- Rhinitis
- Pneumonia
- Scurvy
- Oxidative conditions
Long-Term Smoking Effects
Although smoking can have immediate effects, it also comes with many risks, including those that last a lifetime. Smoking has the potential to lead to a shorter life expectancy. Heart and lung issues are often associated with smoking and can lead to strokes, heart attacks, and lung complications like mesothelioma, which can influence your life expectancy. More than 16 million Americans live with a smoking-related disease. The long-term effects of smoking include:
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Lung disease
- Diabetes
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Emphysema
- Chronic bronchitis
- Tuberculosis
- Eye disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Immunocompromised
How Smoking Affects Your Heart and Blood Vessels
Risks of smoking also include cardiovascular complications. The cardiovascular system includes everything from your heart to your blood vessels and greatly affects the functions of the body. Smoking can influence your heart rate and your blood vessels. Additionally, because your blood vessels carry blood throughout the body, smoke toxins also travel throughout the body. According to the CDC, even those who smoke fewer than five cigarettes a day can show early signs of cardiovascular disease.
When the body inhales the smoke, blood vessels become damaged, thicker, and narrower. These factors lead to your blood pressure rising, blood clots forming, and blood vessel bursts. Because of this, smoking is a massive risk factor for strokes and coronary heart disease.
Types of Smoke Smoking Effects
All smoke contains particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. Other chemicals and toxins in smoke may include aldehydes, acid gases, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), benzene, toluene, styrene, metals, and dioxins. Chemicals can abrade internal body parts and lead to scarring. These chemicals can lead to the development of cardiovascular and respiratory issues.
Secondhand Smoke
According to the CDC, secondhand smoke exposure contributes to approximately 41,000 deaths in nonsmoking adults and 400 deaths in infants every year. Even those who do not smoke can be affected by secondhand smoke, which is difficult to avoid.
In short, smoke that you inhale from another source is referred to as secondhand smoke. Secondhand smoke can come from another person smoking cigarettes, popular vapes, or simply inhaling smoke outside or on a job site. Secondhand smoke can be just as dangerous as primary inhalation. Either way, chemicals from smoke can lead to diseases like lung cancer and respiratory issues. Inhaling secondhand smoke can increase the risk of:
- Strokes
- Lung cancer
- Mesothelioma
- Heart disease
- Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS)
- Respiratory infection
- Respiratory symptoms
- Severe asthma
Plastic Smoke
Burning plastic gives off toxic fumes and smoke, which is not only bad for the environment but also for the people left to inhale it. Burning plastic in open fields is a primary source of air pollution. Scientists have proven that particle pollution from outdoor smoke and smog can cause lung cancer. This is because when plastic is burned, it releases toxic gases such as dioxins, furans, mercury, and polychlorinated (BCPs).
Plastic smoke contributes to air pollution by releasing black carbon soot. This toxic soot settles on crops and water and can be inhaled or ingested. Plastic smoke increases the risk of conditions like:
- Heart disease
- Asthma
- Emphysema
- Rashes
- Nausea
- Headaches
- Nervous system issues
- Smoker lung
- Lung Cancer
- Death
Wood Smoke
Wood smoke contains air pollutants such as benzene, formaldehyde, acrolein, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Smoke from burning wood is made of gases and fine particles which can be inhaled or ingested. Wood smoke can be common in professions such as outdoor work or even those who are homeless and rely on fire for food and heat. When these fine particles enter your eyes, mouth, or respiratory system, you may experience side effects like burning eyes, runny nose, and more severe illnesses like bronchitis. These particles may also trigger:
- Asthma attacks
- Heart attacks
- Stroke
- Irregular heart rhythms
- Heart failure
- Chronic bronchitis
Types of Smoking
There is a wide variety of smoking methods on and off the market. Smoking has the potential to lead to smokers’ diseases such as smoker’s lung, lung cancer, stroke, and mental health side effects. Common methods of smoking include:
- Cigarettes
- Cigars
- E-cigarettes
- Hookahs
- Pipes
- Bidis
- Kreteks
- Others
Dangers of Smoking Cigarettes
Cigarettes are the cause of more than 480,000 deaths in the U.S. each year, meaning smoking tobacco cigarettes is the cause of one in five deaths. According to the CDC, more than ten times as many U.S. citizens have died prematurely from smoking cigarettes than those who have died in all the wars fought by the U.S.
Cigarettes are the most commonly used tobacco product in the U.S. and are responsible for the majority of tobacco-related conditions and deaths. Cigarettes are primarily composed of tobacco, over 600 chemical additives, a filter, and paper wrapping. When burned, smokers are exposed to over 7,000 chemicals, many of which are thought to be direct causes of cancer. Smoking tobacco is on
Dangers of Smoking Marijuana
Marijuana has many names, such as cannabis, weed, and pot. The marijuana drug consists of dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The cannabis plant has over 100 cannabinoids, some of which are mind-altering, like THC, and others that do not, like CBD.
Although marijuana is the most used federally illegal drug in the U.S., many states have begun legalizing it. People often smoke marijuana through paraphernalia, such as bongs, joints, blunts, pipes, bowls, and even vape pens, which have been linked to lung cancer. Just like many other drugs, marijuana smoke inflames and irritates the lungs. Smoking marijuana regularly could lead to the same adverse health effects as those who smoke cigarettes. Those who smoke marijuana are even vulnerable to developing lung cancer.
Dangers of Cigar Smoking
Although similar to other tobacco products, cigars are described as a roll of tobacco wrapped in lead tobacco or another tobacco-containing product. The three primary types of cigars sold in the U.S. are large cigars, cigarillos, and small cigars.
Historically, cigar smoking has been associated with older men. However, with the few laws surrounding flavored cigars, younger generations are beginning to use them more. For example, according to the CDC, U.S. cigars were the second most commonly used tobacco product among U.S. middle and high school students in 2022.
Cigars are just as toxic and contain just as many chemicals as cigarettes. Cigars are a primary cause of lung cancer and other serious conditions such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Effects of Inhaling Toxic Chemical Smoke
People can accidentally inhale toxic chemicals through gases, dust, and smoke as a result of a chemical reaction through heating, reactions, or explosions. An especially toxic group of chemicals are VOCs, Volatile Organic Compounds. VOCs can be found in the home in objects such as carpets, paints, varnishes, caulks, and upholstered furniture. The side effects of inhaling toxins can develop quickly or lead to long-term effects.
Short-term effects of inhaling toxic smoke include:
- Respiratory issues
- Headaches
- Fainting
- Nausea
- Hemoptysis
- Eyesight difficulties.
The long-term effects of smoking include:
- Chronic coughs
- Damaged nerves
- COPD
- Low concentration
- Memory problems
- Other severe issues
Treatment Options for Smokers
If you still smoke, there are treatment options available to help you quit as well as combat smoking-related diseases. If you are a non-smoker affected by secondhand smoke or have quit smoking and were diagnosed with a disease like lung cancer, there are medical treatments available. Whether you are a current smoker or you are in smoking cessation, there are treatment options for your side effects.
If you are a current smoker seeking medical treatment, there may be complications with therapies. Smoking weakens the body, meaning smoking while undergoing cancer treatment decreases the effectiveness of therapies. Additionally, smoking while undergoing treatment can make the body more susceptible to medication and cancer side effects.
Counseling for Smokers
Across the world, some coaches and groups provide counseling for smokers. These counselors can help you create a plan to quit smoking as well as provide support for stress and withdrawal. For smokers who do not use tobacco, therapy is an excellent option to discuss how to quit.
Medication for Smokers
To help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings, medication can help. There are many over-the-counter medications, such as patches, gum, and lozenges, that help combat side effects. Additionally, there are prescription forms of Nicotine Replace Therapy (NRT) inhalers, nasal sprays, varenicline, and bupropion to weaken withdrawal symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions About Smoking Effects
- Is Secondhand Smoking Worse Than Smoking? Secondhand smoke is not necessarily worse than smoking but can be just as dangerous. Inhalation of secondhand smoke occurs when someone nearby is smoking and you inhale their smoke. Secondhand smoke often affects people in occupations such as firefighting, the military, and other high-exposure jobs. Unfortunately, secondhand smoke inhalation often affects infants and others who cannot control their distance from smokers. Secondhand smoke can lead to heart and lung conditions as well as health defects in children and infants.
- How Smoking Affects Your Heart and Blood Vessels – Smoking permanently impacts the cardiovascular system, including your heart and blood vessels. This is because when you inhale, the oxygen travels through your lungs and into your heart, where it is pumped throughout the rest of your body through your blood vessels. When you smoke, the chemicals you inhale also travel throughout your body to your heart and blood vessels, damaging them and leading to cardiovascular diseases.
- Can Smoke Effects Cause Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis is contracted when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Smoking can increase the risk of contracting tuberculosis (TB), a bacteria that attacks and infects the lungs. Additionally, smoking can encourage a recurrence of tuberculosis and impair the body’s response to TB treatment.
- Is Vaping Safer Than Smoking a Cigarette? Vaping, or smoking an electric cigarette, is relatively new to the world, and there is very little known about its smoking effects. There are over 2,000 chemicals in most vapes, many of which are directly linked to causing cancer. Just like smoking regular cigarettes, e-cigs have been found to increase the risk of lung cancer, mesothelioma, and cardiovascular issues. Many people switch from cigarettes to vaping, but there are some vapes with over five times as much nicotine as a regular cigarette.
Get Your Lung Cancer Case Evaluation
If you have more questions about how smoking may affect your health or you have been diagnosed with a smoking-related disease like lung cancer, Lung Cancer Center has the resources to help. Receive your free case evaluation to determine if you are eligible for a lung cancer settlement.


