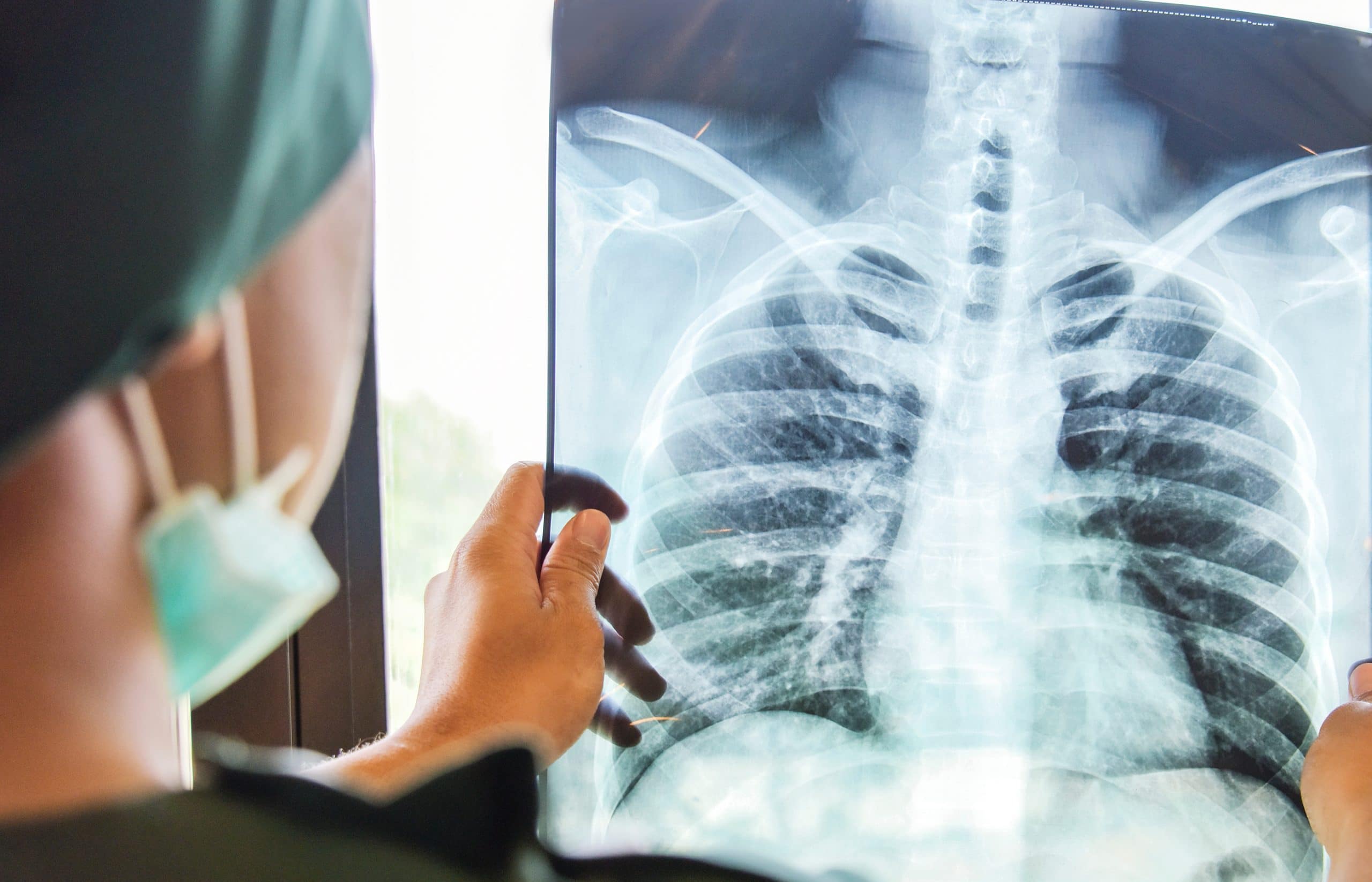
What Causes Lung Cancer?
Cigarettes aren’t the only cause of lung cancer. While they are the most prominent, there are dozens of chemicals and substances (known as carcinogens) that have been proven to cause cancer. Learn more about the different cancer-causing agents.

What Are The Causes of Lung Cancer?
One of the most frequently asked questions for lung cancer patients besides how to avoid lung cancer is what caused my lung cancer. Tumors that develop in the lungs cause lung cancer, and there are various factors that contribute to its development. These causes include exposure to cancer-causing compounds known as carcinogens. At work, school, or in your home, you or a loved one may be exposed unknowingly to a number of carcinogens every day. These carcinogens can include dangerous gases, such as radon, or even building materials that use hazardous chemicals or products, like asbestos. Once exposed for a long period, it can be very difficult to prevent lung cancer.
Hazardous Chemicals
Exposure to certain chemicals can pose a serious threat to human health. Much of these chemicals can be found on job sites and in old or poorly maintained building structures, including residences. The owner or manager of the contaminated structure is responsible for adequately removing the pollutant before allowing anyone to enter the premises, leading to negligent exposure.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the government agency in charge of enforcing hazardous exposure and environmental quality regulations, though companies have slipped through the cracks and defied laws previously. If you or a person you know was exposed to a harmful substance while on the job, it could be due to corporate negligence, and you may be entitled to a settlement or compensation. Hazardous chemicals and other products can include:

Lung Cancer from Asbestos
Once known for its durability, fire resistance, and cost-effectiveness, many referred to asbestos as a “miracle mineral” (pre-1982) and used in many different construction capacities. People primarily used asbestos as insulation for pipes, boilers, automobile brake linings, and more before scientists discovered it to be carcinogenic.
Bundles of fibers that make asbestos, when disturbed and crumbled into small particles, can be extremely dangerous. If something expels the fibers into the air, they can become lodged in a person’s lungs, irritate the tissue over time, and eventually cause the cells to mutate and develop into a type of lung cancer. However, doctors have linked asbestos to mesothelioma diagnoses, a rare disease that affects the lining of the lungs as well as other parts of the body. Medical professionals sometimes misdiagnose mesothelioma as lung cancer since it is not as common.

Does Radon Cause Lung Cancer?
The second leading cause of lung cancer is exposure to a poisonous, naturally occurring, radioactive gas called radon. What makes the gas so dangerous is its lack of color and odor. Radon causes approximately 21,000 lung cancer deaths every year. Typically, the gas oozes out of the soil and into the air. Usually, bits of radon float throughout the environment in many places outside. However, it only becomes dangerous in concentrated environments, such as inside houses and other residences.

Uranium and Lung Cancer
Energy professionals have used another mineral, uranium ore, as an abundant source of concentrated energy for over 60 years. Uranium naturally occurs in rocks and seawater. Generally, miners send uranium to processing plants to utilize for nuclear energy. The energy this method supplies adds up to about 11 percent of the world’s annual electricity. The U.S. military also uses uranium to power nuclear plants and reactors, in radioisotopes, and as a source of fuel.
Since this mineral is radioactive, exposure to high concentrations of enriched uranium for extended periods can cause healthy cells to mutate and begin multiplying excessively. This process has been known to cause lung cancer as well as other types of cancer. Fortunately, depleted or naturally occurring uranium has never specifically caused any human cancer.

Arsenic and Lung Cancer Risk
Arsenic is abundant in the environment, and miners often find it as a natural element in soil, rocks, water, air, plants, and animals. Typically, humans take in low levels of arsenic when we breathe, drink water, and eat food. However, this exposure is less dangerous. When people breathe in arsenic, it could put them at risk of developing lung cancer.
Before 1985, manufacturers used arsenic in several human-made products – primarily pesticides and herbicides. This fact put those who transported, applied, or worked around these toxic products at high risk for exposure to dangerous levels of arsenic. Those spending a lot of time around former agricultural sources of arsenic, older industrial buildings, or coal processing plants are also at high risk of dangerous arsenic exposure.

Cadmium Exposure and Lung Cancer
Classified as a carcinogen in 1993, cadmium is another element that occurs naturally, and many can find it in small amounts in air, water, soil, and food. All soils and rocks, including fertilizers made from coal and minerals, host cadmium. Scientists extract cadmium when producing zinc, lead, and copper. Manufacturers also use it for batteries, pigments, metal coatings, and plastics.
Those who work in factories where cadmium products are made or those who ingest cadmium products such as secondhand tobacco smoke and cadmium-contaminated foods are more likely to have a dangerous level of exposure to the element. Cadmium exposure has been known to be among the causes of lung cancer as well as prostate, pancreatic, and kidney cancer.

Can Chromium Cause Lung Cancer?
Research has shown that long-term exposure to chromium can increase the risk of developing lung cancer in patients. There are two types of chromium: trivalent chromium (known as Cr III) and hexavalent chromium (known as Cr VI). This element is most toxic in its Cr VI state, primarily targeting the respiratory tract, but Cr III can be an essential element in humans.
Chromium was popular in industrial capacities, and manufacturers used it primarily for making steel or other alloys as well as dyes, pigments, leather, wood preservation, and chrome plating.

How Does Nickel Cause Lung Cancer?
Mined from the earth’s crust, this element, although carcinogenic, scientists commonly combine it with other elements to form nickel compounds that have a wide range of industrial uses. Its excellent corrosion and heat resistance, durability, and strength make it ideal for use in metal alloys, which account for most of its usage.
In factories and plants where they produce nickel, toxic exposure to the substance is likely. Factory exposure could occur in manufacturing, mining, smelting, welding, casting, and grinding. Nickel can cause lung cancer when people inhale its particles through fumes or by skin contact.
Petroleum and Lung Cancer
It’s in our gasoline, and we commonly use it in rubber and tires, refrigerators, life jackets, and anesthetics. Petroleum, also known as petrolatum, is crude oil that’s also a fossil fuel. Much like other fossil fuels, such as coal, petroleum is made from the remains of ancient marine organisms. These organisms included ocean plants, algae, and bacteria. When plants and animals sank to the seafloor at the end of their lifecycle, their remains (fossils) developed into carbon-rich substances after millions of years of extreme heat and the pressure from being crushed by tons of layers of sediment and plant debris. Today, scientists find petroleum in massive underground reservoirs where ancient seas once thrived.
As a source of energy, petroleum presents some challenges due to its tendency to release toxic gases, such as carbon dioxide, when burned. Medical professionals feel that prolonged inhalation or exposure to petroleum products can lead to lung disease and cancer. It is important to explore alternative and sustainable sources of energy that do not pose such risks to human health and the environment.

Particle Pollution
Particle pollution or smog is a significant cause of lung cancer in non-smokers. Dirty truck exhausts and smoke from power plants and chimneys often cause this type of pollution. The air we breathe can contain a mix of small, toxic liquid particles that are too small to see. Prolonged inhalation of such air in toxic environments can shorten your life and even lead to lung cancer. First responders like firefighters encounter particle pollution and smog a lot, as they are the first ones on the scene. California is the state with the highest levels of particle pollution in the nation, with Pennsylvania coming in a close second. It is crucial to take measures to reduce particle pollution and improve air quality to protect our health.
Lung Cancer from Smoking
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest types of cancer, with smoking being the leading cause of almost 80-90% of all lung cancer deaths. When an individual smokes, whether it’s cigarettes, e-cigarettes, marijuana, or any other substance, the healthy cells in their body begin to divide rapidly. This abnormal division of cells hinders their normal functioning, leading to tumor growth. Therefore, it’s essential to begin your journey to smoking cessation to decrease the risk of lung cancer and other related health issues.
Family or Personal Lung Cancer Genetics
It is unfortunate that genetic factors, independent of exposure to environmental risk factors, can cause lung cancer. Research suggests that individuals with a family history of lung cancer may have a higher risk of developing the disease due to rare inherited mutations in lung cells. It is important to be aware of your family medical history and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider in order to take appropriate preventive measures and improve your chances of early lung cancer detection and treatment.
How to Prevent Lung Cancer
Reducing the risk of lung cancer is possible through certain measures. If you are a smoker or are exposed to secondhand smoke, it is crucial to eliminate this exposure as soon as possible. Furthermore, limiting your exposure to hazardous materials, such as radon and potential cancer-causing chemicals, can be helpful. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and maintaining a balanced diet, you can enhance your overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of developing lung cancer.
What’s Next on Your Lung Cancer Journey?
If you suspect that you may have early symptoms of lung cancer and have been exposed to any known carcinogens, it is important to visit your doctor right away for early screening and diagnosis. Your doctor may administer imaging and blood test biomarkers to detect any signs of lung cancer or other illnesses. Early detection is key, as it allows for more treatment options and an increased chance of successful treatment. Don’t wait – take action as soon as possible to ensure your health and well-being.