What Causes Smoker Lung?
By Madeline May |
Smoking can pose a severe threat to a person's lungs, making it difficult to breathe and function. Smoking can increase the risk of numerous conditions like smoker lung. Learn about the symptoms and treatments for smoker lungs.

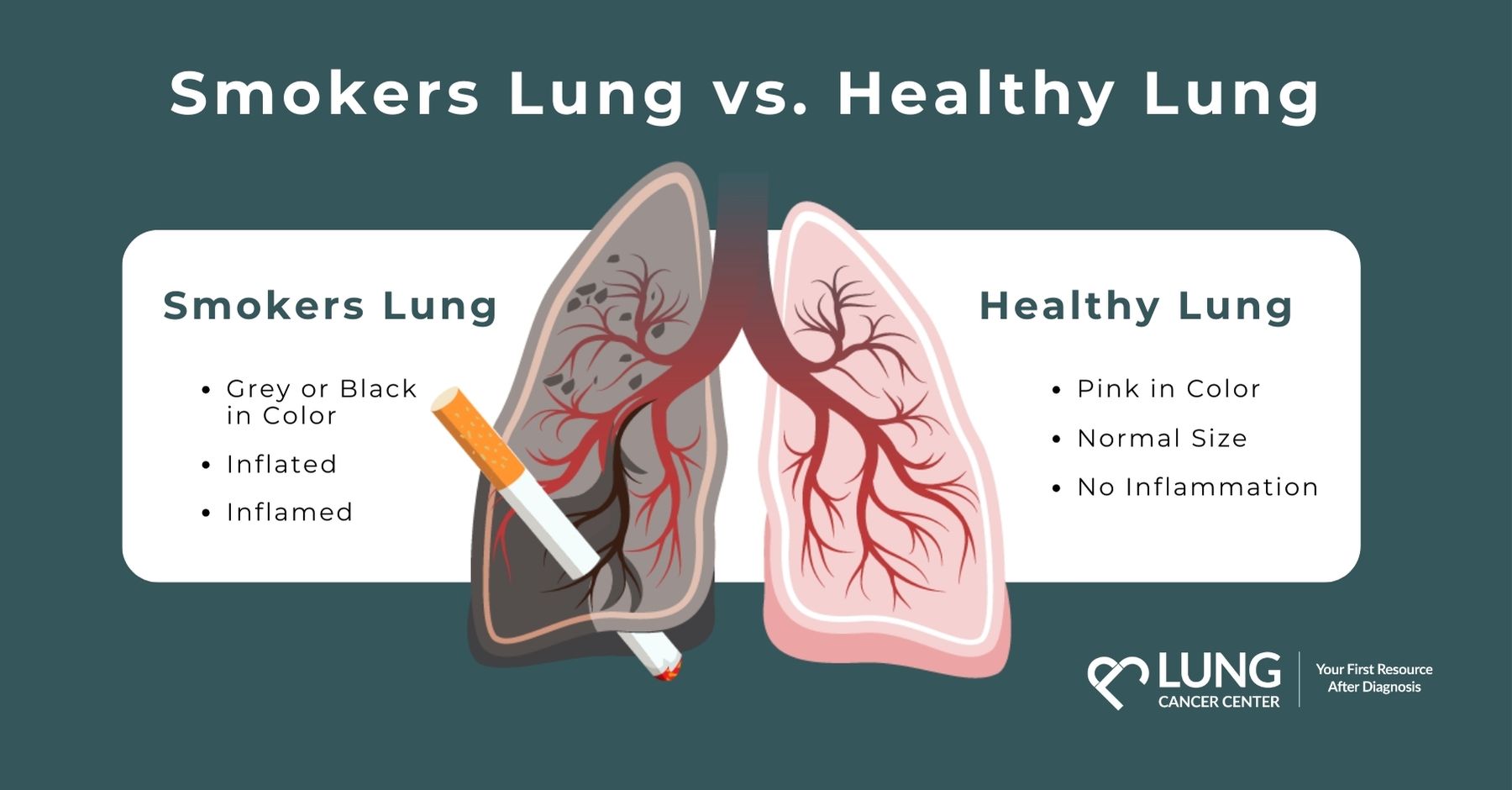
Smoker Lung vs Healthy Lung
“Smoker lung” or “smokers’ lungs” refers to the visible and functional damage caused by long-term smoking. Unlike healthy, pink lungs that are elastic and efficient, smokers’ lungs are often gray or black, filled with tar, and struggle to perform essential functions. When a person smokes, each inhale introduces over 7,000 chemicals into the lungs, nearly 70 of which are known carcinogens. These toxic substances cause inflammation, excess mucus, and permanent scarring, severely affecting lung performance over time. This makes regular healthy living more difficult and even more so if you are dealing with another respiratory illness.
In a healthy lung, cilia—small hairlike structures—work to clear out dust and particles, while alveoli, tiny air sacs, allow for oxygen exchange. However, in a smoker’s lungs, nicotine paralyzes and destroys these cilia, preventing the removal of harmful particles and allowing mucus buildup that leads to conditions like chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, and emphysema. Tar from cigarettes builds up, turning lung tissue black and contributing to blockages that make breathing increasingly difficult.
While quitting smoking is challenging, the body begins to heal almost immediately. Lung function improves over time, though some damage may be irreversible. In this article, we will help you understand the differences between smokers’ lungs and healthy lungs and how individuals can seek treatment and legal options.
| Healthy Lungs | Smoker Lung |
| Pink Color | Gray or Black Color |
| Normal Size | Hyperinflated |
| Zero Inflammation | Inflamed Patches |
| Dome-Shaped Diaphragm | Muscle Loss in Diaphragm |
What Is Smoker Lung Disease?
Smoker lung disease encompasses a range of serious respiratory conditions resulting from prolonged exposure to the harmful chemicals found in cigarette smoke. Key illnesses include chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The toxic substances in cigarette smoke cause significant inflammation and excessive mucus production in the lungs, which, combined with the destruction of cilia, severely impair respiratory function.
These changes lead to persistent symptoms such as chronic coughing, shortness of breath, and a heightened risk of respiratory infections like pneumonia. Understanding smoker lung disease is essential for recognizing the severe consequences of smoking and the importance of early intervention for improving lung health.
Smoking can increase the risk of other lung diseases, too. Regular smokers experience an increased risk for lung cancer, esophageal cancer, and worsening of their mesothelioma condition. Smoking also increases the risk of other respiratory conditions like COPD and pneumonia. In the United States, about 80% of all COPD-related deaths are traced to smoking.
What Are the Symptoms of Smoker Lung?
Symptoms of smoker’s lung can vary based on the type of smoke inhaled, the duration of exposure, and whether the exposure was firsthand or secondhand. Common symptoms include persistent coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, and an increased frequency of lung infections. Other signs may include hoarseness, pain in the shoulders, arms, and hands, and unexplained fevers.
The impact of smoking is staggering, with more than 480,000 deaths attributed to tobacco use each year—equating to one in five deaths. This grim reality not only affects physical health but can also take a toll on mental well-being.
Can Lung Damage From Smoking Be Reversed?
While lung damage from smoking can be significant, some effects can improve after quitting. Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to enhance life expectancy, which can lead to immediate benefits for lung health, although complete reversal of damage is not always possible.
Conditions like emphysema cause permanent damage by destroying the tiny air sacs in the lungs. However, inflammation and scarring can improve thanks to the lungs’ remarkable ability to heal. The sooner you quit, the sooner your lungs can recover, leading to improved lung function and reduced respiratory infection risks.
If you’re ready to quit, numerous resources, including counseling and support groups, are available. To increase your chances of success, set a quit date, share your decision with friends and family, identify and avoid triggers, find healthy coping strategies for stress, and seek professional help. Quitting smoking is one of the most beneficial actions for your health and quality of life.
How to Detox the Lungs for Recovery
To support lung health and recovery, patients should avoid secondhand smoke and harmful chemicals from vaping. Preventing infections, maintaining a nutritious diet, and exercising regularly can strengthen lung function. While the concept of a “detox” may not be scientifically supported, adopting these lifestyle changes and seeking appropriate treatment can aid in the journey to becoming a lung health survivor.
Taking the Next Steps Towards Recovery From Smoker Lung
Recognizing the effects of smoking on your lungs, particularly in relation to smoker’s lung and lung cancer, is an important step in your recovery journey, especially if you’ve been diagnosed with a respiratory condition. If you have concerns about your lung health, our dedicated team of patient advocates is ready to assist you. They can provide support in navigating effective treatment options and pursuing legal compensation, ensuring you have access to the resources you need for recovery.
By quitting smoking and seeking professional medical care, you can significantly enhance your lung health and overall well-being. It’s important to remember that it’s never too late to address smoker’s lungs and take proactive steps toward a healthier future. Reach out to our patient advocates to learn about the steps you can take to reclaim control of your health. With our experience supporting individuals affected by lung cancer and mesothelioma due to toxin exposure, we understand the challenges you face and are committed to helping you through this process. Contact us to see how we can help.