Pericardial Mesothelioma
Pericardial mesothelioma, accounting for a small percentage of mesothelioma cases, is a cancer that impacts the lining of the heart, known as the pericardium. It develops due to contact with asbestos, a naturally occurring mineral that was commonly used in construction and industrial settings for its fire-resistant properties. Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests like CAT scans to detect abnormalities in the pericardial area.
What Is Pericardial Mesothelioma?
Pericardial mesothelioma is a type of cancer that affects the lining around the heart, called the pericardium. The pericardium has two layers: one directly attached to the heart (visceral layer) and the other forming the outer sac around the heart (parietal layer). Pericardial mesothelioma specifically impacts these layers. Even though it is rare, having pericardial mesothelioma can feel like a death sentence. Cancer of the heart can be an alarming and emotionally unbearable reality to face. Luckily, our experts and contributors have experience dealing with people who have contracted pericardial mesothelioma and have gathered the below information to help people combat this horrible disease.
In comparison to other types of mesothelioma, pericardial mesothelioma is one of the more uncommon ones, accounting for only 1% to 2% of all cases. This rarity is attributed to the limited potential for asbestos particles to reach the protective membrane. However, when asbestos fibers do manage to get stuck into the pericardium, they cause irritation and inflammation, leading to the formation of tumors. In the rest of this article we will dive into the causes, treatment opportunities, and general prognosis of this disease.
What Causes Pericardial Mesothelioma?
Pericardial mesothelioma is most often caused by asbestos exposure and while asbestos exposure is considered a risk factor, the connection is not as clear-cut as with other forms of mesothelioma. Pericardial mesothelioma develops through a complex physiological process. The process begins with the initial inhalation or ingestion of the asbestos fibers either thorough work or day to day life. When someone inhales or swallows asbestos, the fibers could get stuck in different areas of the body, including the pericardium. Erionite, a mineral fiber akin to asbestos, has also been linked to known to cause mesothelioma.
Once lodged in the lining, both of these fibers can trigger chronic inflammation and scarring. Prolonged inflammation can lead to genetic mutations in the pericardial cells, causing them to overproduce and form cancerous tumors within the sac. These tumors can grow and spread, invading nearby tissues and structures. In advanced cancer stages, mesothelioma of the pericardium may metastasize to other organs and tissues in the body.
What Is the Most Common Cause of Pericardial Effusion?
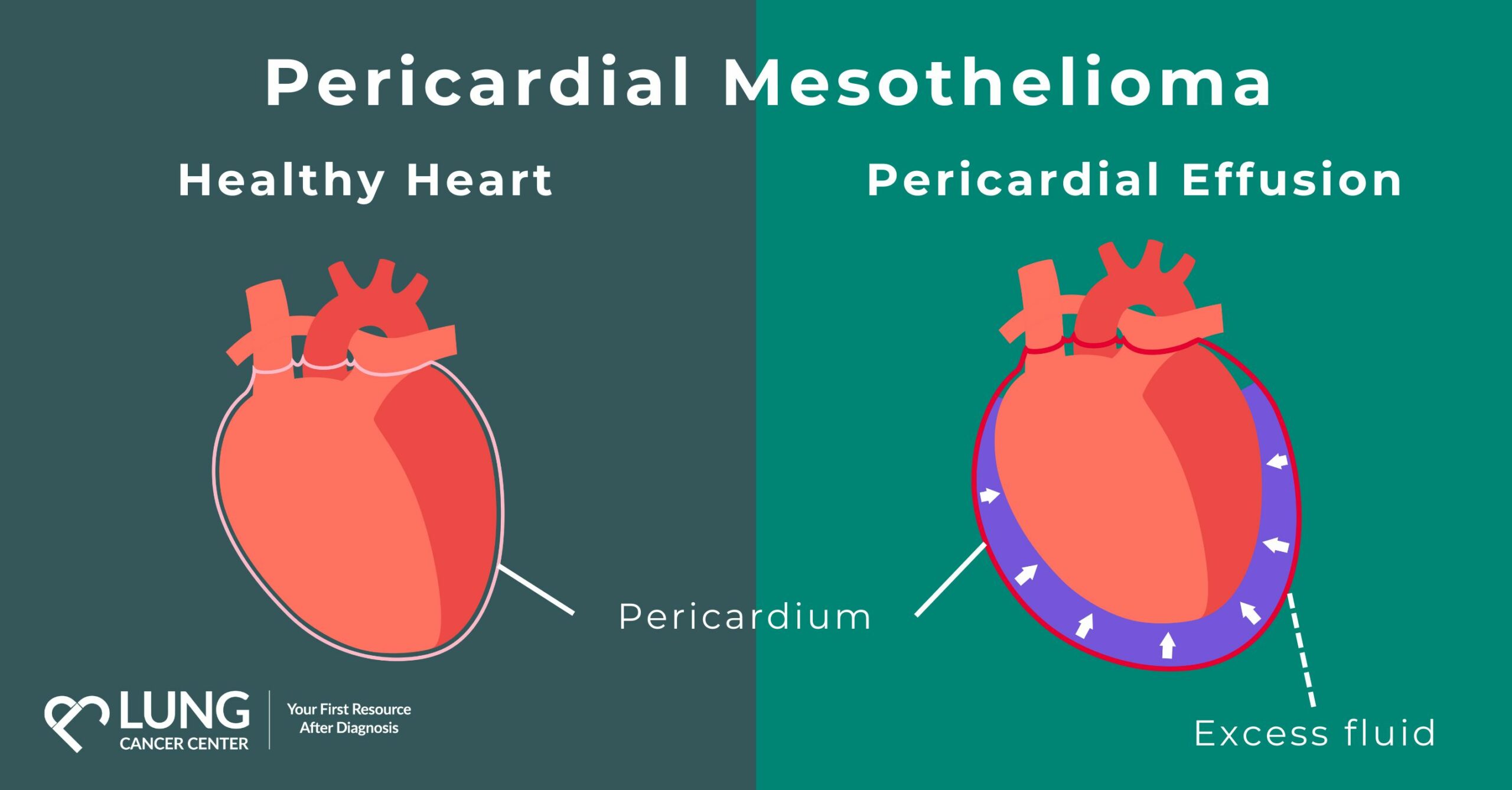
Infections and auto-immune disorders are common causes of pericardial effusion. However, pericardial mesothelioma can also cause pericardial effusion. As the cancer cells multiply and spread, they can irritate the pericardium, leading to inflammation. This inflammation triggers the release of extra fluid into the pericardial space, creating a pericardial effusion. The fluid accumulation puts pressure on the heart, causing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
What Happens to a Person with a Damaged Pericardium?
The pericardium provides protection and lubrication of the heart. If you experience damage to the pericardium, it can lead to various complications, such as infection, inflammation, or intense medical interventions. The specific outcomes for a damaged pericardium depend on the cause and severity of the damage. One potential consequence of a damaged pericardium is the development of pericardial effusion, which is the accumulation of excess fluid in the pericardial sac. Severe or rapidly progressing pericardial effusion can cause life-threatening conditions that restrict the heart’s ability to function properly. Treatment options may include medications to reduce inflammation, draining excess fluid around the heart, or surgery to repair or remove damaged portions of the pericardium.
Damaged Pericardium Symptoms
A damaged pericardium can result in pericarditis, inflammation that triggers various symptoms affecting the heart’s function. The primary symptom is chest pain, often exacerbated by deep breaths, coughing, or lying flat. Relief may be found by leaning forward while sitting. The severity varies, with acute pericarditis emerging suddenly and typically resolving with treatment within a few weeks. Chronic pericarditis, persisting for over three months, poses a more serious threat. Constrictive pericarditis, a rare complication, involves a thickened pericardium restricting the heart’s ability to fill with blood, potentially leading to heart failure. Despite pain being a common symptom, it’s not the only symptom.
Pericardial Mesothelioma Symptoms
Pericardial mesothelioma symptoms can be challenging to identify early on due to how vague they can be and how often they may be misdiagnosed as another heart problem, such as heart disease. It’s important to note that the following symptoms can also be caused by other conditions that isn’t related to mesothelioma at all. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms though, it is important to see a doctor to get a diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are important for improving the chances of a successful outcome. Common mesothelioma and heart symptoms associated with pericardial diseases may include:
- Sharp Chest Pain
- Difficulty Breathing
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Fatigue and Unexplained Weakness
- Fever and Night Sweats
- Pericardial Effusion
The latency period between asbestos exposure and the onset of symptoms can last several decades, making it challenging to diagnose and treat. Mesothelioma misdiagnosis can occur in cases affecting the pericardium, leading to delayed or inaccurate identification. Seeking early detection of pericardial mesothelioma is crucial for treatments to be effective in treating this aggressive cancer.
Think you were exposed to asbestos? Fill out a free case evaluation form today.
How to Diagnose Pericardial Mesothelioma
Diagnosing pericardial mesothelioma involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging tests, and biopsies to confirm the presence of cancer. Due to the extreme rarity, the pericardial mesothelioma diagnostic process involves the work of oncologists, cardiologists, radiologists, pathologists, and other specialists.
The process starts with a healthcare provider reviewing your medical history, noting any known asbestos exposure. Then, they will conduct a physical examination to assess symptoms and cardiac and lung function. When necessary, CT scans and MRIs are done to detect abnormalities in the pericardium and surrounding tissues. Ultimately, a biopsy determines if cancer is present. If pericardial effusion occurs, your doctor may extract the fluid and examine it for cancer. Without the occurrence of pericardial effusion, biopsies are done through a needle or surgical method.
How Can You Treat Pericardial Mesothelioma?
Given the rarity of pericardial mesothelioma, there is no established standard treatment protocol. Treatment approaches are often based on individual circumstances. Once confirmed, a pericardial mesothelioma diagnosis involves a collaboration of doctors to address and focus on managing symptoms and pain. Similar to standard lung cancer treatments, certain individuals may need surgical intervention, specifically a pericardiectomy involving the removal of part or all of the pericardium to alleviate symptoms. Other treatment options may include chemotherapy or radiation therapy to control the spread of cancer cells and shrink tumors.
What Is the Prognosis for Pericardial Mesothelioma?
Patients with pericardial mesothelioma typically experience a poor prognosis. The disease’s rarity can lead to delayed identification, limiting the effectiveness of treatment options compared to other forms of mesothelioma. According to recent clinical studies, the pericardial mesothelioma life expectancy ranges from 6 months to a year, with some patients living longer.
Pericardial mesothelioma tends to be more aggressive, rapidly invading surrounding tissues and organs. Certain factors, such as older age, advanced stage at diagnosis, and the extent of tumor involvement, can affect the malignant mesothelioma prognosis. Early intervention, combined with palliative care measures can improve symptoms and enhance the quality of life for those affected by mesothelioma.
Occupational Cancer Legal Resources
Cancers such as mesothelioma and lung cancer can be caused by exposure to various carcinogens and harmful substances during employment. Other than asbestos, several substances in certain workplaces may contribute to the development of cancer, including radon, arsenic, cadmium, diesel exhaust, and silica dust. Certain occupations pose a higher risk of cancer compared to others when they involve regular exposure to known carcinogens.
Lung cancer affects workers in industries such as construction, mining, manufacturing, and chemical processing. In cases where occupational exposure leads to cancer, you may have legal options to seek compensation from employers or responsible parties. Legal professionals specializing in asbestos-related cases play an important role in helping individuals obtain compensation to cover medical bills and other costs associated with cancer. Legal action involving mesothelioma revolves around establishing a link between the disease and exposure to asbestos or other causes. Many cases result in settlements, while others may proceed to trial. Our legal attorneys are always ready for trial and can help you out if needed today.